-
 WhatsApp: +86 19941574798
WhatsApp: +86 19941574798
-
 sale06@kfqizhongji.com
sale06@kfqizhongji.com
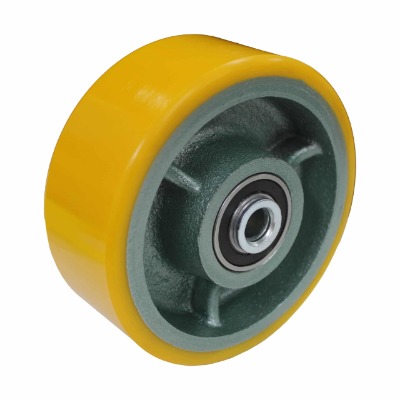
Mold-on Polyurethane Wheels
Mold-on polyurethane wheels are industrial wheels manufactured by firmly bonding polyurethane material to a metal or plastic core via a molding process.
Mold-on polyurethane wheels are industrial wheels manufactured by firmly bonding polyurethane material to a metal or plastic core via a molding process. Leveraging their unique production technology and material properties, they are widely used in industrial and commercial applications. Below is a detailed introduction to their core information:

Core Structure and Manufacturing Process
Wheel Core: Common materials include cast iron and die-cast aluminum, providing a robust load-bearing foundation. For example, some models adopt precision cast iron cores for enhanced strength, while others use die-cast aluminum cores to balance strength and lightweight design.
Polyurethane Coating: The outer layer, usually with a hardness of approximately 95 Shore A, offers a balance of elasticity and wear resistance.
Molding Process
During production, the wheel core is first placed in a specialized mold. Heated liquid polyurethane raw material (with low viscosity) is then injected into the mold, where polymerization is triggered by the mold temperature. Finally, the polyurethane not only takes shape but also forms a strong chemical bond with the wheel core surface. This molding process eliminates the risk of detachment common in conventional bonded wheels, delivering significantly higher connection stability than traditional assembled wheels.
Balanced Load-Bearing Capacity and Floor Protection
Polyurethane material combines elasticity and hardness. When paired with a high-strength core, it exhibits excellent load-bearing performance. For instance, a 12×3-inch cast iron core mold-on polyurethane wheel can achieve a dynamic load capacity of 3,500 pounds. Meanwhile, its elastic properties reduce impact on floors, making it suitable for factory and warehouse surfaces without causing scratches.
Wear Resistance, Damage Resistance, and Versatile Environmental Adaptability: These wheels outperform ordinary rubber wheels in wear resistance, cut resistance, and resistance to oil and grease. They are compatible with various environments, including atmospheric media, and environments containing alcohol and ethylene glycol. However, they should be avoided in environments with organic acids, inorganic acids, alkaline solutions, and saturated steam.
Smooth Operation and Low Noise: The elasticity of polyurethane cushions vibrations, and when combined with ball bearings or roller bearings, ensures smooth rolling—ideal for equipment requiring continuous movement. Additionally, they significantly reduce operating noise, making them suitable for noise-sensitive environments such as food processing facilities and warehouses.
Wide Temperature Range Adaptability: Most products can operate within a temperature range of -45°F to 180°F (-43°C to 82°C), effectively coping with high and low-temperature fluctuations in industrial settings and adapting to different regional and workshop conditions.
Typical Application Scenarios
Industrial Material Handling: As core components for forklifts, hand trucks, and logistics turnover carts, some bracket-equipped models are suitable for light to medium-heavy load scenarios. For example, models with welded steel brackets are designed for light loads, while those with steel plate brackets are for medium-heavy loads.
Commercial and Specialized Equipment: They serve as accessories for catering industry food delivery carts and cold storage transfer equipment, and also act as replacement parts for industrial machinery. For instance, 6×2-inch models are specifically designed as high-strength equipment replacement wheels, suitable for heavy-duty applications such as material handling and warehousing.
Common Specifications and Optional Configurations
Specifications: Available in various sizes, with common diameters ranging from 4 to 12 inches and widths from 2 to 3 inches. Wheel bearings ensure smooth rolling.
Optional Configurations: Offer multiple mounting and braking options, such as swivel casters with top plate mounting, models with side brakes or cam brakes, and rigid wheels/swivel wheels—meeting installation and operational requirements of different equipment.
Categories
Recent Cases
Recent Products
Recent Blogs
- How Do Polyurethane Wheels Compare To Metal Wheels
- Why Choose Injected Polyurethane (TPU) Wheels for Your Equipment
- Why Roller Coasters Use NDI Polyurethane Wheels
- How to Choose a Poly Wheels Manufacturer That Won't Fail
- Why Polyurethane is the Choice for Pallet Jack and Forklift Wheels
- Pallet Stacker Drive & Idler Wheels for Automated Warehouses
- Mold-on Polyurethane Wheels
- Analysis of the Causes of Cleanroom Stacker Polyurethane Wheel
- Why Are NDI Drive Rollers the Premier Choice for Pallets
- Polyurethane Wheels in Mining












What Industries Benefit Most From Using Polyurethane Industrial Wheels
Why Roller Coasters Use NDI Polyurethane Wheels