-
 WhatsApp: +86 19941574798
WhatsApp: +86 19941574798
-
 sale06@kfqizhongji.com
sale06@kfqizhongji.com
Analysis of the Causes of Cleanroom Stacker Polyurethane Wheel
The "powdering" and "degumming" phenomena of the polyurethane travel wheels used in the cleanroom stacker (stocker) are common fault problems, especially in high-cleanliness and high-precision semiconductor or electronic factories.
The "powdering" and "degumming" phenomena of the polyurethane travel wheels used in the cleanroom stacker (stocker) are common fault problems, especially in high-cleanliness and high-precision semiconductor or electronic factories, which have extremely high requirements for equipment stability and wheel cleanliness. The following are the key and subsequent improvement suggestions for such problems:
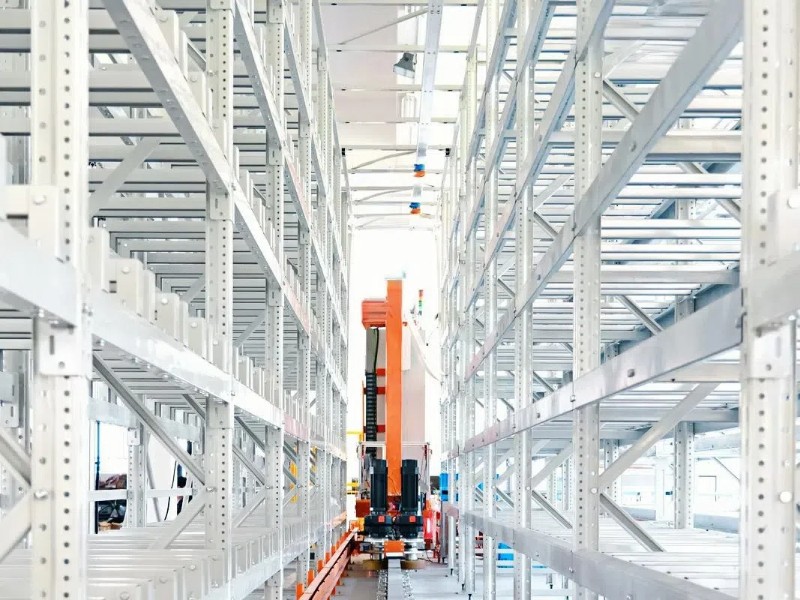

1. The cause of powdering
The polyurethane material is not clean or bubbles are generated during the production process, resulting in an unstable molecular structure.
Long-term use in scenes with high temperature, strong ultraviolet rays, low temperature, dryness, or chemical substances
The walking system is overloaded or the impact is too large
The rough ground causes the polyurethane surface to quickly necrotize and heat up, promoting powdering.
2. Degumming reasons
The adhesive layer and the wheel core are not firmly bonded, which may be due to insufficient pre-bonding treatment (such as insufficient degreasing and grinding). Improper selection of adhesives or lax process control leads to pressure and degumming between the adhesive layer and the metal/composite wheel core.
Polyurethane is an insulating non-elastic body, and the heat generated cannot be dissipated in time. As the temperature rises, the bonding force will gradually weaken, eventually leading to failure. The generation of this energy is related to the load and speed of the tire and the physical properties of the tire (such as diameter, width, and thickness).
3. Subsequent transformation suggestions
• Material optimization
Use a high-wear-resistant, low-dust clean-grade polyurethane formula (such as ester-based high-crosslinked structure or all-solid thermosetting PU).
Require suppliers to provide material certification that meets the clean room Class 10~100 level (such as ISO 14644-1 certification).
• Process improvement
Perform surface or chemical roughening before bonding to improve the surface activity of the wheel core.
Use high-strength, high-temperature resistant adhesives, and strictly control the curing temperature and time.
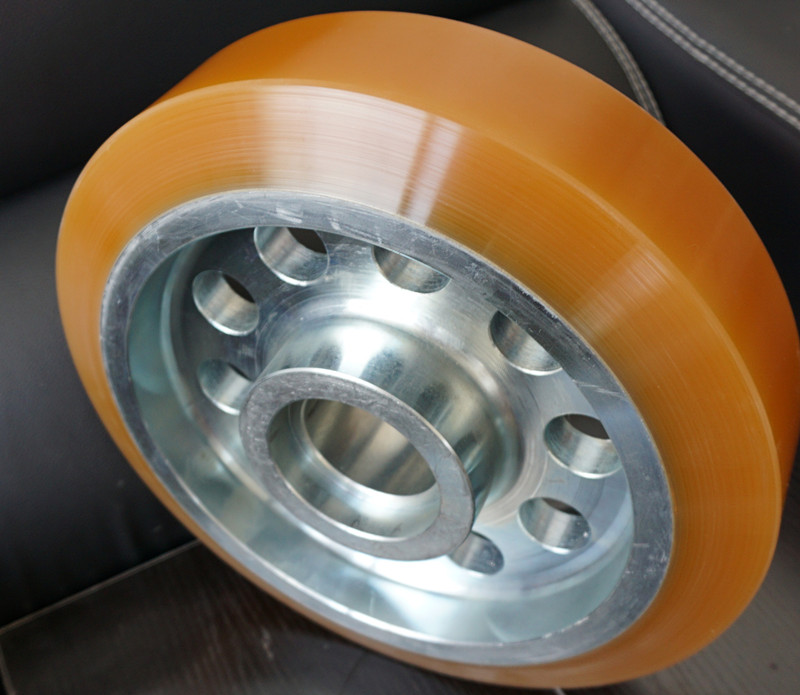

• Structural optimization
Adopt a dual structure of mechanical fixing + bonding (such as keyways, and urethane coating) to enhance shear strength.
Design a reasonable rubber coating thickness and buffer layer to disperse the distribution and prevent concentrated distribution from debonding.
• Use and maintenance optimization
Strictly control the equipment running speed and load to avoid long-term high-intensity continuous operation
Clean the ground regularly to prevent foreign matter from entering the wheel-rail contact surface.
Establish a wheel life replacement cycle to prevent excessive use.
• Supply chain control
Choose a professional manufacturer with experience in the development of cleanroom wheels to provide customized materials and structural designs
Require wheel suppliers to provide fatigue test reports, bonding strength tests, and other data support.
Philson polyurethane wheel manufacturer has many years of experience in the manufacture of cleanroom polyurethane wheels, advanced polyurethane casting equipment, different types of polyurethane formulas, and experienced engineers, and can customize wheels that meet the requirements of harsh environments according to your usage.
Categories
Recent Cases
Recent Products
Recent Blogs
- How Do Polyurethane Wheels Compare To Metal Wheels
- Why Choose Injected Polyurethane (TPU) Wheels for Your Equipment
- Why Roller Coasters Use NDI Polyurethane Wheels
- How to Choose a Poly Wheels Manufacturer That Won't Fail
- Why Polyurethane is the Choice for Pallet Jack and Forklift Wheels
- Pallet Stacker Drive & Idler Wheels for Automated Warehouses
- Mold-on Polyurethane Wheels
- Analysis of the Causes of Cleanroom Stacker Polyurethane Wheel
- Why Are NDI Drive Rollers the Premier Choice for Pallets
- Polyurethane Wheels in Mining












Are Heavy-Load Poly-Coating Wheels Quiet on Hard Floors
Why Polyurethane is the Choice for Pallet Jack and Forklift Wheels